Ancient Egyptian Medicine: Pioneers in The Medical Field In The Oldest Civilization
The ancient Egyptians were the first people who document medicine. From the beginnings of civilization in the late fourth millennium BC until the Persian invasion of 525 BC. Ancient Egyptian medical practice included simple non-invasive surgery, setting of bones, dentistry, and an extensive set of pharmacopoeia. Egyptian medical thought influenced later traditions, also the Greeks.
The medical historian Warren R. Dawson said that Egypt possesses the earliest known medical texts, experimental surgeries, and medical terminology. Egyptians were the first to contribute to the advancement of medicine, with medical practices dating back over five thousand years. This timeline is unsurprising, given the Egyptians’ advanced knowledge in mathematics, engineering, and architecture, evidenced by their monumental structures such as the pyramids.
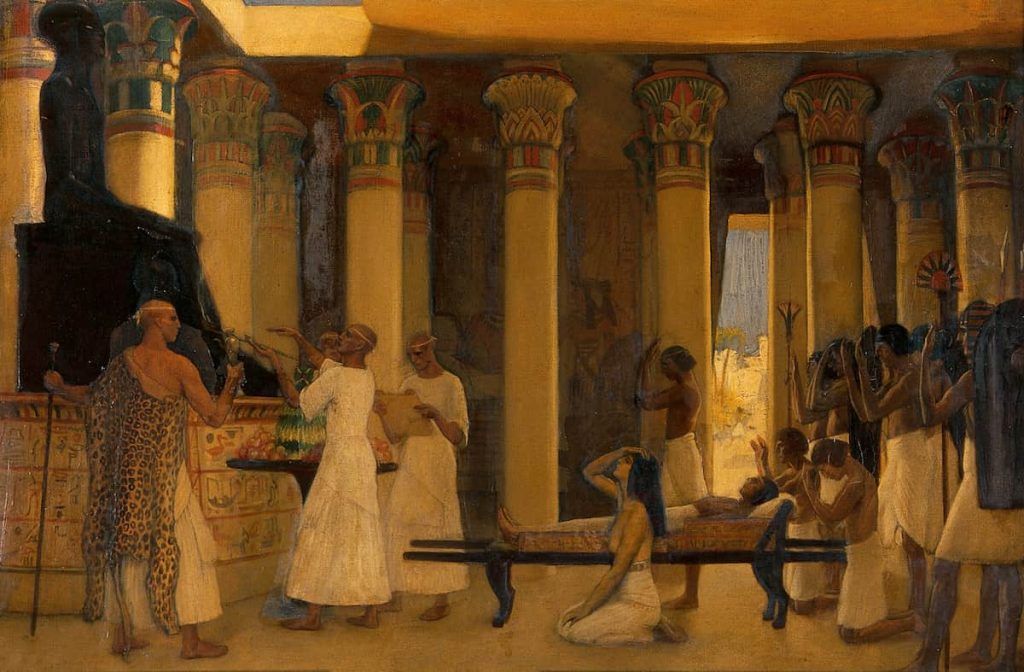

The Beginning Of Ancient Egyptian Medicine
The Greek historian Herodotus visited Egypt around 440 BC and wrote of his observations of their medicinal practice. Pliny the Elder also wrote about them in a historical review. Hippocrates (the “father of medicine”), Herophilos, Erasistratus, and later Galen studied at the temple of Amenhotep. The ancient Egyptian medicine also contributed to Greek medicine.
Moreover, the ancient historian Herodotus wrote that influential rulers like Cyrus and Darius employed Egyptian physicians, indicating the high esteem in which Egyptian medical practitioners were held. These physicians documented their treatments. Then this knowledge remained through generations. So many of their ancient methods like with practices in modern medicine.
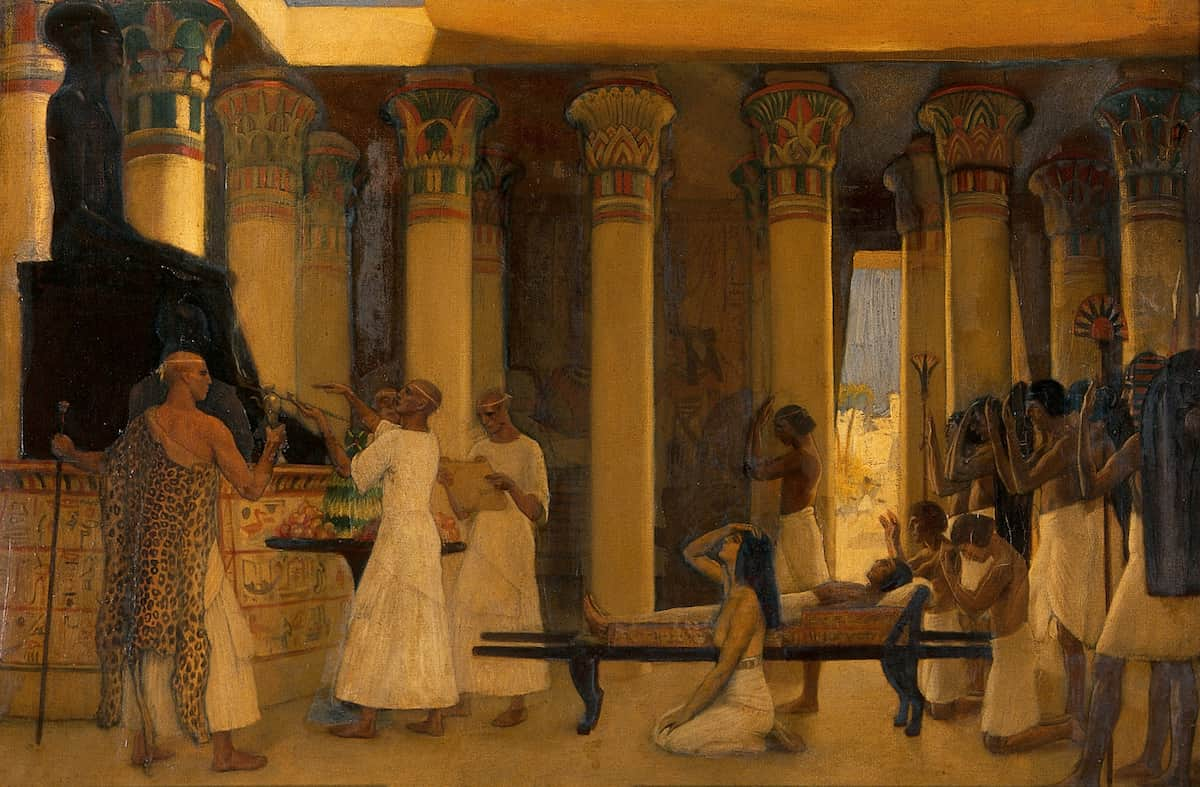
Treasures On The Walls of Egyptian Tombs
Egyptians also knew other information, which comes from the images that often adorn the walls of Egyptian tombs and the translation of the inscriptions. The development of modern medical technology also contributed to the understanding of ancient Egyptian medicine. So, Paleopathologists were able to use X-rays and later CT scans to view the bones and organs of mummies. Electron microscopes, mass spectrometry, and various forensic techniques allowed scientists unique glimpses of the state of health in Egypt 4000 years ago.
Nutrition in Ancient Medicine
The ancient Egyptians were at least partially aware of the importance of diet, both in balance and moderation. Because of Egypt’s great endowment of fertile land, food production was never a major problem, although paupers and starvation still exist. The main crops for most of ancient Egyptian history were emmer wheat and barley. Egyptians consumed
1- the wheat in the form of loaves, which were in a variety of types through baking and fermentation, with yeast greatly enriching the nutritional value of the product. One farmer’s crop could be enough for twenty adults.
2- Barley also existed in beer.
3- Vegetables and fruits of many types existed widely.
4- They also produced oil from the linseed plant, and there was a limited selection of spices and herbs.
5-Meat like sheep, goats, pigs, and wild game was regularly available to at least the upper classes, and they used fish widely, although there is evidence of prohibitions during certain periods against certain types of animal products; Herodotus wrote of the pig as being ‘unclean’.
What Medicine Did Ancient Egyptians Use?
The ancient Egyptians used honey medicinally. Moreover, the juice of the pomegranate was an astringent and was also consumed for its taste. Over 800 remedies are listed in the Ebers Papyrus; some of the treatments were applied topically, with ointments or wrappings, and others were to be taken orally in the form of pills or mouth rinses; some were even inhaled.

Ancient_Egyptian_medial
The recipes to cure constipation consisted of berries from the castor oil tree, Male Palm, and Gengent beans, just to name a few. One recipe that was to help headaches called for “inner-of-onion, fruit-of-the-am-tree, natron, setseft-seeds, bone-of-the-sword-fish, cooked, redfish, cooked, skull-of-crayfish, cooked, honey, and abra-ointment.
The Egyptians also used animal feces and even some metals as treatments. These prescriptions of antiquity were measured out by volume, not weight, which makes their prescription-making craft more like cooking than what pharmacists do today.
Pharmacology In Ancient Medicine
The ancient Egyptians discovered the medicinal properties of plant life around them. The Edwin Smith Papyrus contains many recipes to help heal different ailments. One short section of the papyrus lays out five recipes:
1- one dealing with problems women may have had.
2- three techniques for refining the complexion.
3- the fifth recipe for ailments of the colon.
The oldest metal (Bronze or copper) surgical tools in the world were in the tomb of Qar. Surgery was a common practice among physicians as treatment for physical injuries. The Egyptian physicians recognized three categories of injuries: treatable, contestable, and untreatable ailments.
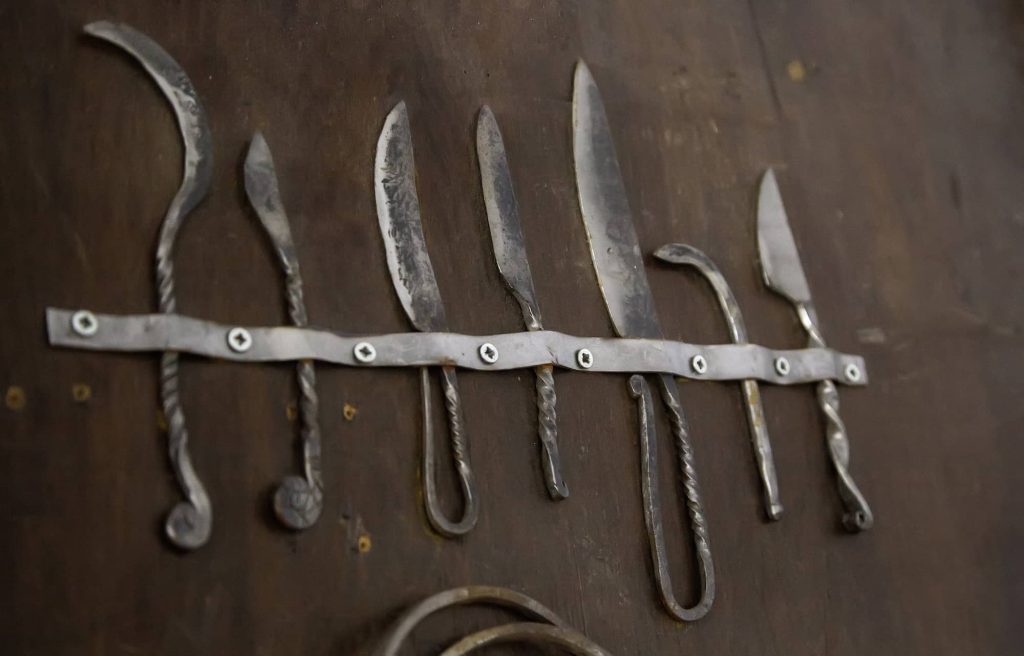

Surgical Tools
Treatable ailments, the surgeons would quickly set to right. Contestable ailments were those where the victim could presumably survive without treatment, and if they survived, then doctors might attempt surgical attempts to fix the problem with them. They used knives, hooks, drills, forceps, pincers, scales, spoons, saws, and a vase with burning incense.
Moreover, Egyptians used prosthetics, such as artificial toes and eyeballs. They served for decorative purposes.
The extensive use of surgery, mummification practices, and autopsy as a religious exercise gave Egyptians a vast knowledge of the body’s morphology, and even an understanding of organ functions.
Dentistry In Ancient Egyptian Medicine
The dentistry profession dates from the early 3rd millennium BC. The Egyptian diet was high in abrasives from sand left over from grinding grain and bits of rocks in the way bread was prepared, and so their teeth were poor and bad. All Egyptian remains have sets of teeth in quite poor states.
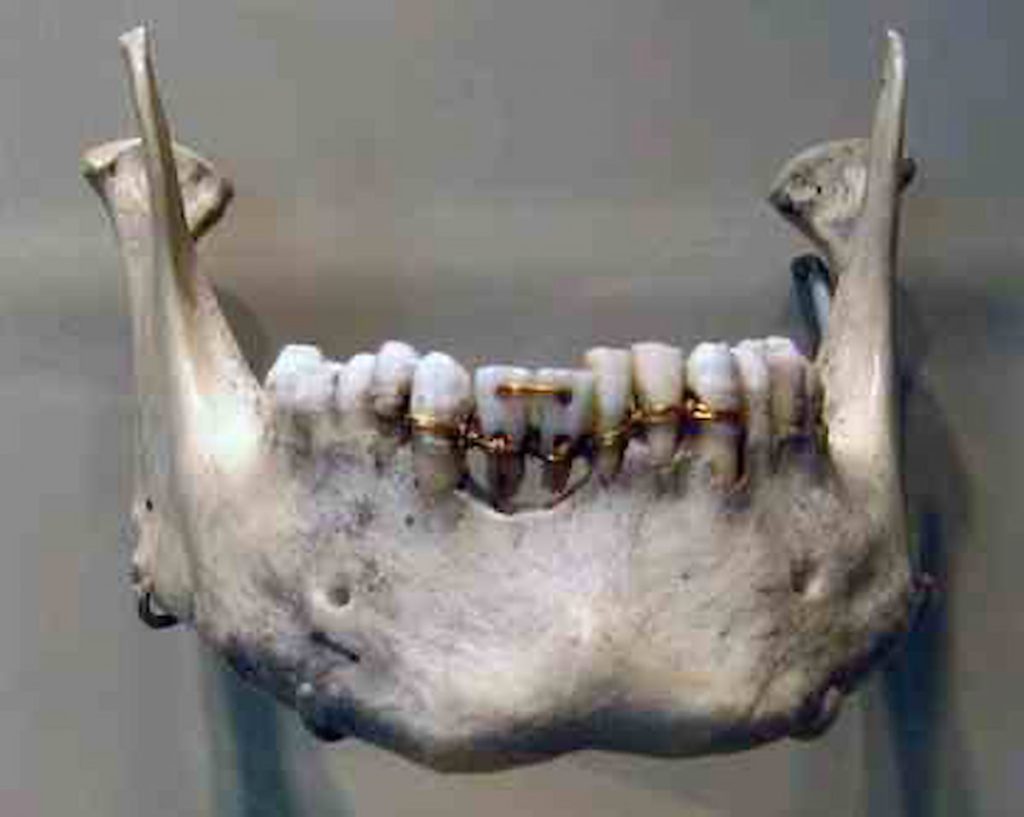
Ancient Egypt Dentistry – Egypt
Dental disease could even be fatal, such as for Djedmaatesankh, a musician from Thebes, who died around the age of 35 from extensive dental disease and a large infected cyst. If an individual’s teeth escaped being worn down, cavities were rare due to the rarity of sweeteners.
Dental treatment was ineffective, and the best sufferers could hope for was the quick loss of an infected tooth. Extreme pain might be little with opium.
The Egyptians also had spiritual beliefs that influenced their medical practices. They attributed certain ailments to gods, demons, and spirits with supernatural powers.
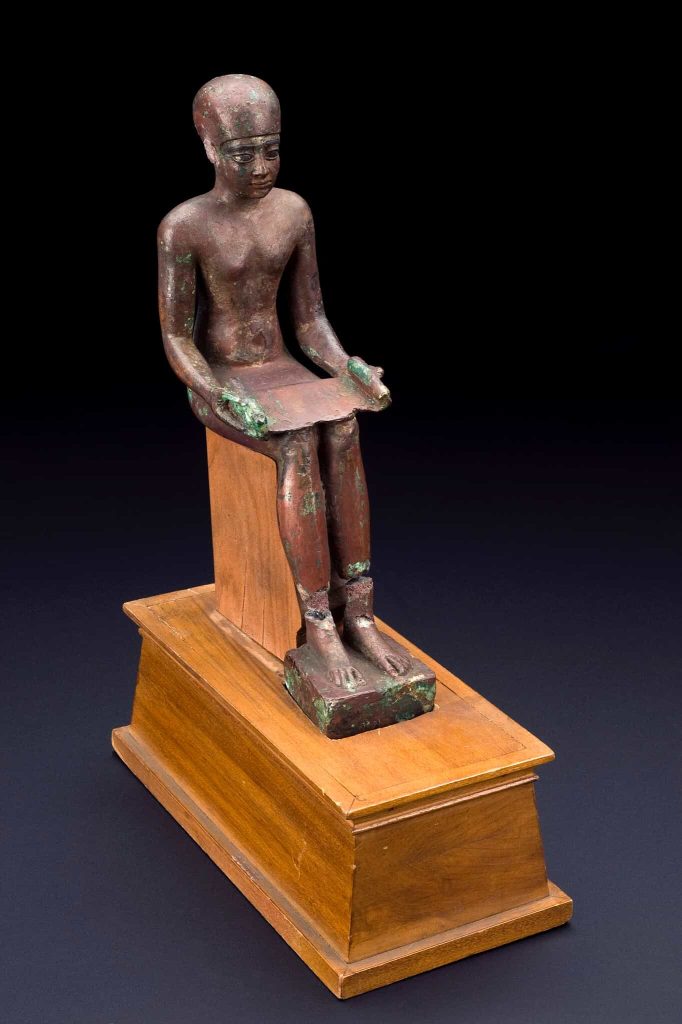

the god Imhotep
The other deity respected by the people as the God of medicine and healing was Imhotep. In the teachings of the ancient Egyptians, the god Imhotep was a person of a few disciplines, specifically, architecture, philosophy, meteorology, and medicine addition to others. He attempted to comment on medical views, making a few remarks about medical surgery, which was performed using primitive implements, other than natural remedies. He also developed a reputation as the best physician in Egypt; he showed compassion for his patients, and at least three shrines were constructed in his honour. These shrines today are now what is vitally important in archaeology, with the efficient lessons of his influence in medicine.
What was the Egyptian Name for a Physician or a Doctor?
The ancient Egyptian word for doctor is “swnw”. This title has a long history. The earliest recorded physician in the world, Hesy-Ra, practiced in ancient Egypt. He was “Chief of Dentists and Physicians” to King Djoser, who ruled in the 27th century BC.
The lady Peseshet may be the first recorded female doctor. She was possibly the mother of Akhethotep, and she was the Lady Overseer of the Lady Physicians.
There were many ranks and specializations in the field of medicine. Royalty employed their doctors, even their own specialists. There were inspectors of doctors, overseers, and chief doctors. Known ancient Egyptian specialists are ophthalmologists, gastroenterologists, proctologists, and dentists.
Conclusion:
Overall, the Egyptian civilization had many achievements in several fields, including arts, science, and medicine. Ancient Egyptians surprisingly had a great knowledge of different medical fields such as anatomy, surgery, and general medicine; they could diagnose and treat several diseases successfully. Hundreds of cases have been mentioned in several medical papyri. The treatment at that time included a huge diversity of sources as plants, animals, and minerals.
Most of our knowledge of this great medicine was from the medical pharaonic papyri, which could be an incredible source to understand and learn several things from such a great civilization. Ancient Egyptians did not have a clear dichotomy between medicine and magic; they considered health and illness resulted from a person’s relationship with the universe, including people, animals, good and bad spirits.















