Ancient Egyptian Military: How Ancient Egypt Built One of the World’s Earliest Powerful Armies
The Ancient Egyptian Military power was developed through the combination of strategy, innovation. Moreover, the will of those pharaohs who considered war as a way to achieve glory and control. Behind every pyramid and temple stood an ancient Egypt army that protected the kingdom and stretched its boundaries far into Africa and the Middle East. The thunder of chariots across desert sands and the cracking volleys of archers under the scorching sun made the ancient Egypt army a force to be reckoned with.
It grew out of militia like bodies into a structured elite army capable of rivaling great empires. Then came legendary campaigns under Pharaohs like Thutmose III and Ramesses II that wrote history. Whether fighting to defend the land of the gods or to acquire lands for themselves, the ancient Egyptian army was the great hand behind one of the greatest civilizations in the world. In this blog, we shed light on more about their soldiers, battles, and weapons.
1- The Rise of the Ancient Egyptian Military
In the early days, Egypt didn’t have a real army, or in other words, it didn’t have an organized one. Moreover, ancient Egypt did not have a full-time army. They were depending on some farmers, workers, and citizens, they are called when needed. Additionally, during the Middle Kingdom (around 2050–1710 BCE), Egypt faced more serious threats from outside. Therefore, this led to make the Pharaohs and rulers during this time to take real steps in building an organized army. To protect Egypt from any threat coming from outside.
But everything changed when the Hyksos invaded Egypt. The Hyksos are a group of people coming from western Asia, with very modern weapons and an organized army. The types of weapons they used were chariots and composite bows, which the Egyptians had never seen before. Therefore, the Hyksos took over some parts of Egypt and showed how weak the Egyptian army that consisted of farmers and workers.
This hit was like a wake-up call that made the Pharaohs decide to train soldiers, make better weapons, and learning new fighting methods and techniques. This makes Egypt more powerful and organized, which Egypt turned from a defensive nation into an offensive one. Pharaohs wanted to stop future threats before they reached Egypt. So, they sent their armies into Nubia, Libya, and the Middle East to take control of more land. This helped Egypt grow into a powerful empire.
The rise of the Egyptian military was not just about defense. It was about learning, adapting, and becoming a strong force that could lead and protect one of the world’s oldest civilizations.
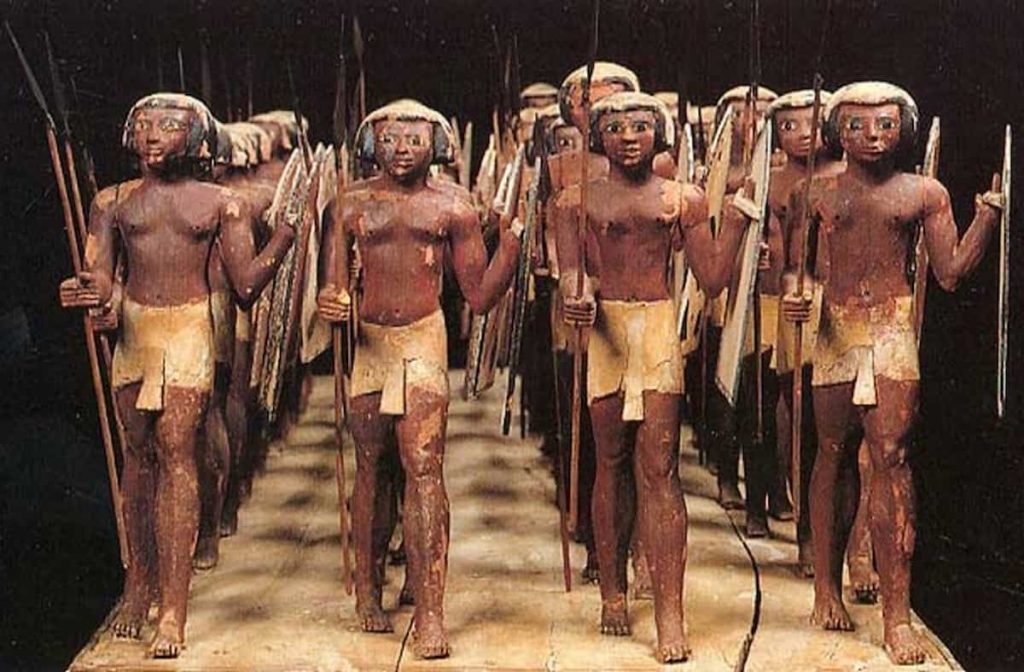

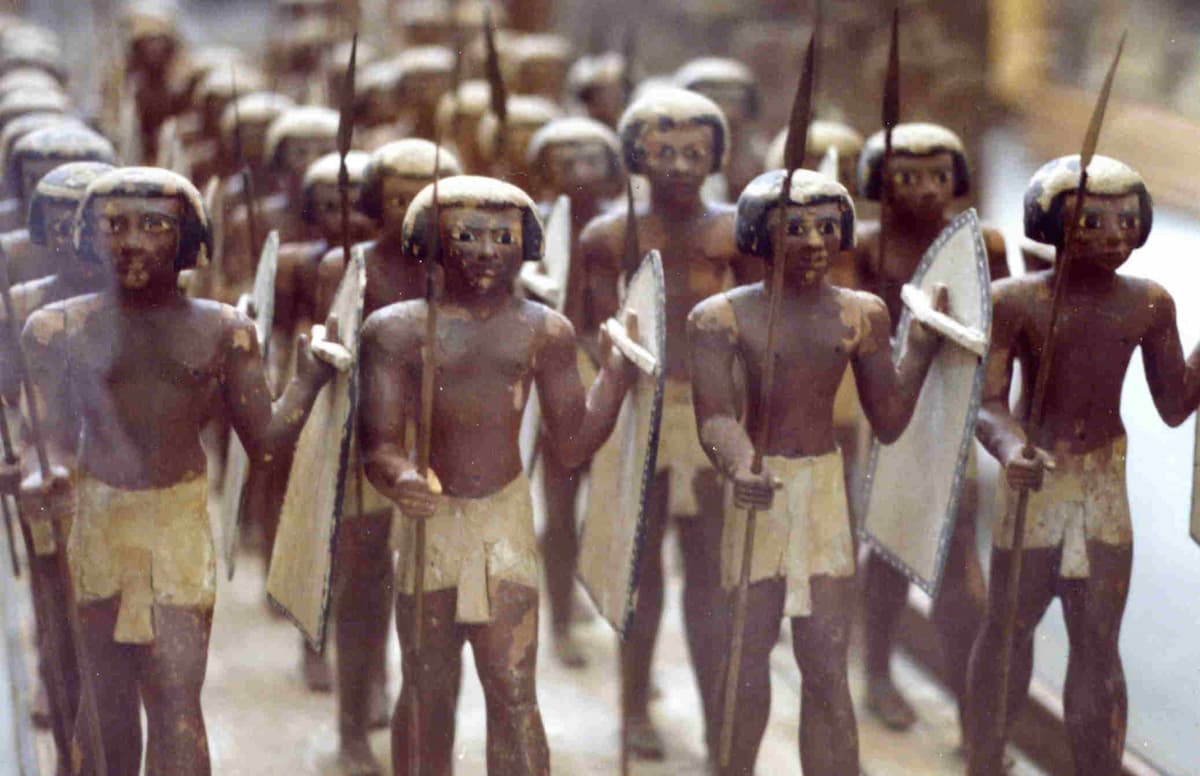
A Group of the Ancient Egyptian Military
2- Weapons of War: The Ancient Egyptian Military Used
The ancient Egyptians had many powerful weapons that they used to guard their land and keep their enemies at bay. Initially, they fought with simple implements like spears, bows, and wooden shields with hides stretched over them. But as stronger enemies weighed upon them, there came the refinement of their weapons.
Most famously, the curved dagger-like sword, the khopesh, was one fine weapon. It was hook-shaped and served well in close combat. The bow and arrow were equally important from a distance. Skilled marksmen could pluck enemies out at distances too far for the ordinary army, and this gave the Egyptian army much credit.
Then bronze weapons were introduced in Egypt, which were far stronger than the stone or copper tools of old. Bronze swords, daggers, and axes gave them might in battle.
But the greatest change came when the Hyksos brought with them the chariot to Egypt. A fast two-wheeled contraption moved swiftly across the desert. Once the Egyptians learned to use them well, they became masters and incorporated chariots into their armed forces, usually with archers mounted on them for added destruction. Improved arms and superior tactics had by now turned Egypt into one of the most feared military powers of the ancient world.

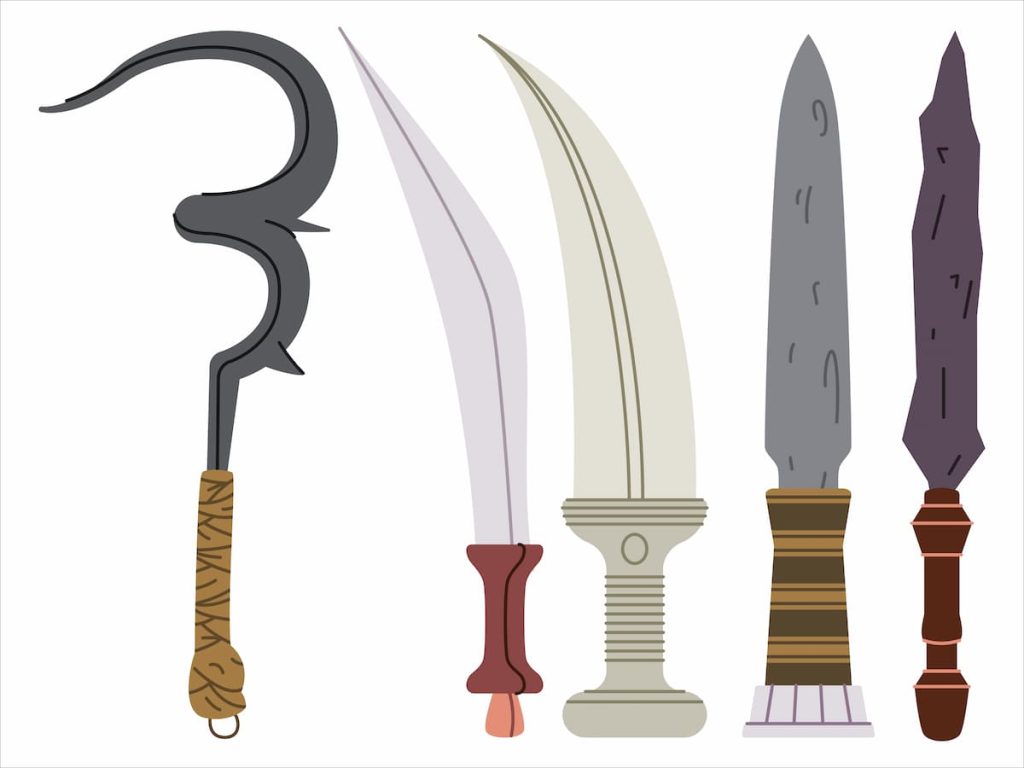
Weapons of War The Ancient Egyptian Military Used
3- The Effective Role of Weapons in Egyptian Society and Warfare
They were not only tools for warfare but also a symbol of political authority. In ancient Egypt, weapons were more than implements of war; they were something significant for society and warfare. Weapons such as spears, daggers, and bows were used by common people in hunting and in self-defense, and sometimes to show a little social status. Wealthy families and soldiers would possess fine bronze weapons adorned with gold or precious stones as marks or symbols of power and wealth; sometimes, such weapons would be buried with their owners, according to some religious beliefs.
Weapons formed the basis by which nations defended Egypt and expanded their territories into foreign lands. The army had to fight off different enemies with khopesh swords, axes, shields, and chariots. With the advent of bronze weapons and chariots, courtesy of the Hyksos, came the huge advantage over the Egyptians. It enabled the army to take the offensive swiftly, hit hard, and keep its enemies behind. The Narmer Palette (3100 BCE) illustrates King Narmer wielding a ceremonial mace, symbolizing his unification of Upper and Lower Egypt. Weapons were similarly tied to religious practices.
Weapons helped the pharaohs extend their boundaries, to control trade routes, and to garner respect from other kingdoms. In a nutshell, weapons helped give shape to Egyptian military might, social order, and even religion. During war, weapons were not just for battle; warfare was a facet of what kept Egypt strong and successful for thousands of years.

Narmer Palette
4- Types of Ancient Egyptian Military Weapons
The ancient Egyptian military was equipped with a variety of weapons, each tailored for particular attacks in the chaos of battle. Most general weapons included spears and javelins. One could throw them at foes or stab in close combat. Another important weapon was the bow and arrow. Skilled archers could shoot from far away, which was a great advantage for the armies in assaults.
The khopesh was a very famous Egyptian weapon: it is still famous as a sort of hook-shaped sword. It was sharp and punishing in close-quarter fighting. Daggers and battle axes were also there and useful in the close-quarter fight. Gradually, these weapons were made stronger with bronze, replacing early implements in stone or copper.
For more protection, soldiers carried shields made mostly from wood and sometimes covered with leather. They could be used for blocking arrows or blows from swords. The greatest change came with the chariot, which the Hyksos brought with them. These were fast two-wheeled vehicles escorting archers running out of control on the battlefield.
Together, these weapons helped Egypt into a strong military force, capable of defending itself and extending its power. Each played its part in transforming Egypt into one of the most powerful ancient civilizations.
Below are some of the most important weapons used in ancient Egyptian warfare:
-
Spears – Used for throwing or stabbing enemies during close fights.
-
Javelins – Lighter spears thrown from a distance.
-
Bows and Arrows – Key for long-range attacks; skilled archers could strike from far away.
-
Khopesh – A curved, hook-shaped sword perfect for close combat.
-
Daggers – Small blades used in hand-to-hand fighting.
-
Battle Axes – Heavy weapons for cutting through armor or shields.
-
Bronze Weapons – Stronger than older stone or copper tools, used to make better swords, axes, and daggers.
-
Shields – Made of wood and leather, used to block attacks.
-
Chariots – Fast, two-wheeled vehicles introduced by the Hyksos, often carrying archers for fast strikes.

Ancient Egyptian Military Weapons
5- How Khopesh Plays a Crucial Role in Changing the Face of Ancient Egyptian Warfare
The khopesh was an extraordinary and important weapon in ancient Egyptian warfare. This curved sword bears a sickle or hook-shaped blade. Unlike the straight sword, the khopesh could both cut and hook away the enemy’s weapon or shield, an immense advantage for close combat.
Before the khopesh, men mostly fought with a spear and a dagger. The khopesh, being heavier and more effective, ensured quicker wins in battles. It could be slashing or pulling an enemy’s shield away, leaving space for an attack. Hence, the khopesh, in the capable hands of a skilled soldier, was something to fear on the battlefield.
The khopesh also became synonymous with power: most pharaohs were equipped with one as a symbol of strength and leadership. Numerous temple reliefs and tomb paintings showed the khopesh. In short, the khopesh revolutionized warfare in ancient Egypt. This gave Egyptians better chances of winning battles and turned Egypt into one of the mightiest civilizations in antiquity.

khopeshes
6- The Ancient Egyptian Military Tactics and Their Weapons
The armies of ancient Egypt won many battles of ancient Egypt army thanks to smart tactics combined with effective weapons. Their armies could fight both on foot and from chariots. To cite an example, archers firing from a distance would be one component of an attack, while infantrymen with spears, shields, and swords would go in slowly, directly to the enemy.
The arrival of chariots with the Hyksos had the effect of changing warfare in Egypt. Charioteers could look across the battlefield, firing arrows or attacking with spears. This speed allowed them to outmaneuver slower foes and deliver attacks where the enemies were least prepared.
Egyptian soldiers would sometimes gather into formations: groups held together tightly, each soldier holding a shield in front or to the side to protect fellow soldiers. Such formations maintained the strength of the army against attacks. Their generals planned battles with care, exploiting terrain and striking at the most opportune moment.
Weapons like the khopesh, bow, spear, and shield were accordingly employed to fit into the tactic; hence, the blending of sound tactics together with formidable weapons rendered the Egyptian army military one of the unchallengeable forces of its day.

The Ancient Egyptian Military Tactics and Formations
7- Victorious Pharaohs: Battles and Campaigns That Shaped Ancient Egypt
Many pharaohs of ancient Egypt were not only rulers but also brave military leaders. They led their armies and fought great battles to defend and extend their empire. These battles helped make history for the land and brought money and power in their wake.
Some of the significant battles in history include the Battle of Megiddo, led by Thutmose III, who planned a surprise attack that depleted their enemies of numerous men and brought new lands under Egypt’s rule. Another famous battle was that of Kadesh between Ramesses II and the Hittites. This may be the largest chariot battle in history. Though it ended in a draw, Ramesses II declared it a great victory and used it as evidence of his might.
Other pharaohs, such as Ahmose I, almost certainly fought to expel the Hyksos from Egypt and to unify Egypt. But rather than simply being a land grab, these battles cemented the notion of the pharaoh as a hero, a leader chosen by the gods.
Victorious pharaohs, using brilliant strategies, strong weapons, and bold leadership, surely helped make Egypt one of the most powerful civilizations of the ancient world.
Long Live Battles
-
Ahmose I – defeated the Hyksos and took back control of Lower Egypt, ending the Second Intermediate Period and starting the New Kingdom.
-
Thutmose III – Known as the “Napoleon of Egypt,” he won the famous Battle of Megiddo, defeating a large group of Canaanite kings.
-
Ramesses II – Led the Battle of Kadesh against the Hittites, one of the biggest chariot battles in history. Though it was a draw, he claimed it as a great victory.
-
Seti I – Fought in Canaan and Syria, winning back many rebellious cities and proving Egypt’s military strength.
-
Merneptah – Fought against the Libyans and Sea Peoples, protecting Egypt from invasion.
-
Ramesses III – Defeated the Sea Peoples in land and sea battles, securing Egypt’s borders during a time of great threat.
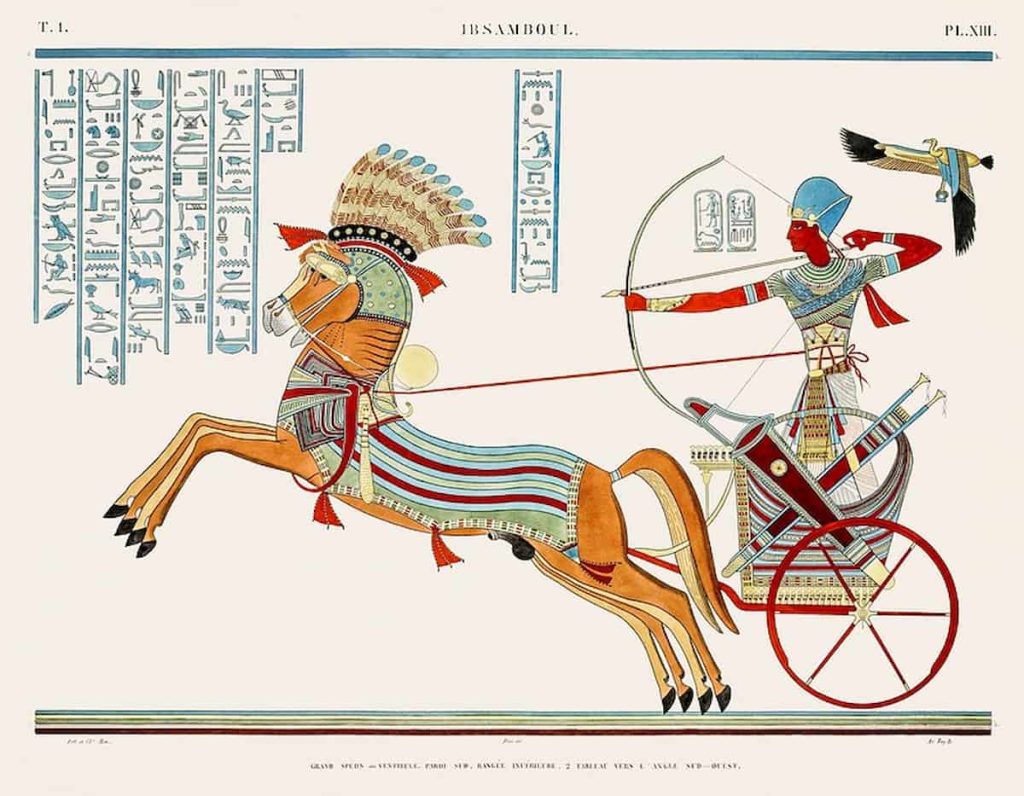
8- How Ancient Egypt Became Organized and Had a Military Organization
The ancient Egyptian military was very well organized and had various corps to carry out specialized duties. The largest corps was that of the infantry, whose core was foot soldiers who transported spears, swords, and shields with which to fight. Being almost the core of the army, these soldiers would stand in the first line in the thick of the fighting. Other important nearby soldiers were the archers, who inflicted damage with bows and arrows from a distance. Later, additional charioteers were introduced into Egypt, who, together with fast chariots, probably moved while eastern archers shot.
Some men in the army were professional soldiers; these trained regularly, received payment from the government, and served for many years. The rest of the men were mostly peasants, drafted into the army, farmers who were called to arms during times of conflict. These men had little training but would snowball out into numbers in times of need.
There was an established chain of command in the army, and this made it extremely vital for discipline and orderliness. Officers issued commands, with higher commanders leading larger units. The army was also divided into divisions that were each accountable for different portions of a battle or the operations of a region. It was this solid organization that made Egypt fight intelligently and win in most battles. With all their roles clearly defined and alongside some competent leadership, Egypt’s army stood as one of the more efficient forces of antiquity.
9- Military Life & Training of The Egyptian Soldiers
The life of the soldier in ancient Egypt was hard but rewarding. Soldiers came from all walks of life. Some were professional forces, trained for battle, while others were peasants who served during times of war. Payment for bravery could be made in cash, food, or land. Some would be given gold; others, homes near a temple or crown estate. Being in the military was becoming a way through which poor men could improve the quality of their lives.
Training was an essential part of military life. Soldiers had to learn the weaponry of spear, sword, and bow. Drills in marching, running, and group combat were also conducted. Physical fitness was another vital area of concern. Soldiers had to obey orders and cooperate in battle. Observing the pharaoh was one of the most important qualities of an Egyptian soldier. The pharaoh was legally regarded as a god as well as a king. Fighting for him was a great honor. Soldiers often swore loyalty to the pharaoh and would be willing to defend the land of Egypt at all costs.
Military life bestowed pride, a sense of purpose, and sometimes fame upon individuals. For thousands of years, it was one of the many factors that brought success to Egypt.
10- Decline and Legacy of the Egyptian Army
The Egyptian army, over time, began to lose its prestige. The New Kingdom was the golden age of Egypt, with mighty pharaohs, armies, and huge territories. However, after countless wars and several leadership changes, the whole thing eventually began to disintegrate. Egypt now stood in peril of threats from the Assyrians, Persians, and later, the Greeks and Romans. Newer armies wore more advanced armor and had improved tactics.
The Egyptian army was declining in power due to poor training, lack of resources, and over-reliance on mercenaries, those very foreign soldiers who are paid to fight. These changes only made it harder for Egypt to stand for itself in defense. The once-great empire was finally overthrown and held by others.
However, so long as her military power lasted, Egypt never left behind a weak legacy. Among the very few cultures that began to use organized armies, chariots, and planned battle strategies, Egypt’s theories and tactics became an inspiration for later civilizations such as the Greeks and Romans.
Today, the world still celebrates the ancient Egyptian soldiers for their brave deeds, the pharaohs for their strength, and their military for their clever fighting. The military history formed a huge basis for making Egypt one of the greatest civilizations in the world.













