The Religion of Ancient Egypt: Beliefs, Gods, and the Afterlife
The religion of Ancient Egypt was a very important part of Ancient Egyptian civilization and community. and a part of the environment. Moreover, numerous deities and gods were thought to be there, each with some importance. These gods were believed to rule over everything, like the sun, rain, floods, health, and even death. The Egyptians believed that through prayer and offerings to the gods, an equilibrium could be maintained for life.
Moreover, the protection of their lands. Ra was the most revered deity, being the god of the sun, who shone and breathed life into the world. The next famous gods would be Osiris, god of the afterlife, Isis, goddess of family and magic, and Anubis, god of mummification. Each town or city had a preferred god or gods, and temples were built to honor them. Also, you can read more about the Ancient Egyptian Gods and Goddesses and learn more about the ancient Egypt facts of religion and myths.
The religion of Egypt was for everyone, and the practicing customs were probably followed at home by the poor as well as the rich. Worshippers also took part in festivals. The concept of Maat, which means truth and balance, was of great importance. The Egyptians thought that those who followed Maat would be rewarded after death. This strong belief in gods and the afterlife helped shape Egypt’s culture, art, and laws for thousands of years. The heart of Ancient Egypt was the religion of Egypt.
1- What Did the Ancient Egyptians’ Religion Believe in?
The ancient Egyptians used to believe in many gods. Moreover, the ancient Egyptian religion was a complicated religious system of beliefs and rituals that shaped a big part of ancient Egyptian culture. Furthermore, it was all about the interactions of the Egyptians with the many deities believed to exist and control the world. On the other hand, the stated number of ancient Egyptian gods was 1,500 deities that were known.
Additionally, rituals such as prayers and sacrifices were offered to the deities to gain their favor. The ancient Pharaohs were the main point that most Egyptians focused on to get their blessing. Besides, these pharaohs were believed they be coming from gods, so you have to obey them and offer gifts. They acted as intermediaries between the people and the gods. And were obligated to support the gods through rituals and sacrifices to maintain ma’at (order) and the functioning of the universe and prevent isfat (chaos).
Isfat (chaos) in ancient Egypt means the Darkness or the Chaos, or the Violence. Furthermore, this word was used in Ancient Egyptian Philosophy.
The individuals could interact with the gods to ask for assistance through prayer or compel the gods to do something through magic. Yes, through magic, popular religious tradition became more prominent throughout Egyptian history as the pharaoh’s status declined. The Egyptians’ belief in the afterlife and the importance of funeral rituals are evident in the great efforts they made to ensure the survival of their souls after death by providing tombs, coffins, and offerings to preserve the bodies and spirits of the deceased.
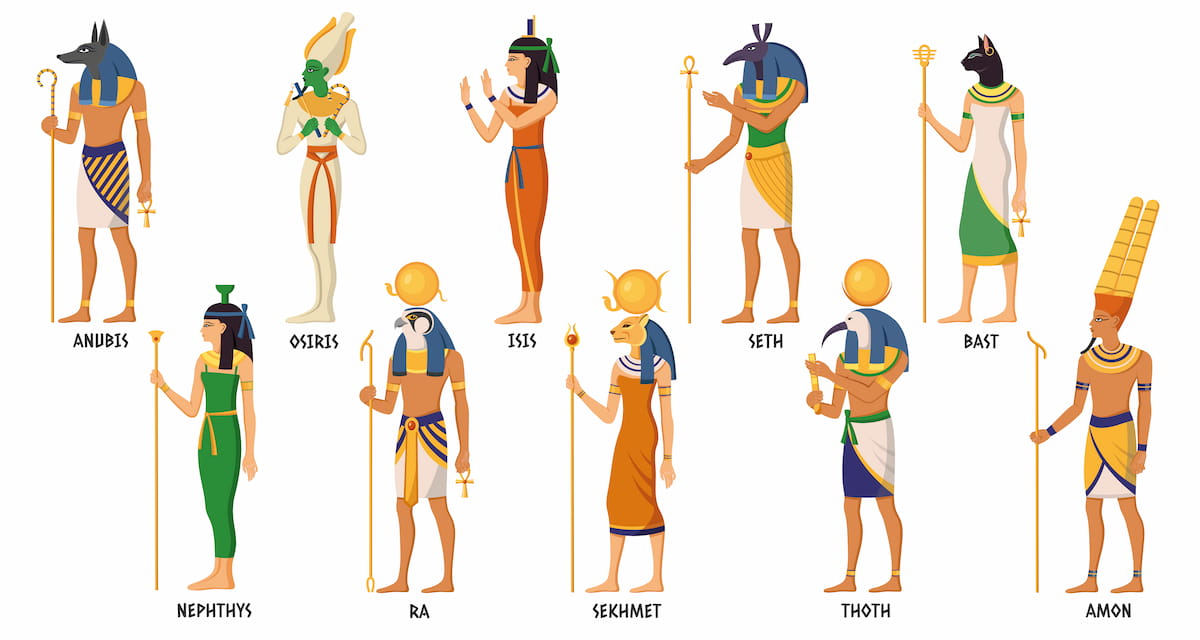
2- The Most Important Egyptian Gods and Goddesses
The Egyptians were polytheists; gods existed in abundance, and each had a distinct function. These gods were associated with every part of Old Egyptian life, from the rising of the sun until death and the afterlife. Some were kind and favorable, whereas others stood for chaos or peril. This amalgamation gave birth to a complex and mighty mythos governing the Egyptians’ way of life and thought.
Ra was the chief god: he was the sun who illuminated the world and gave life. Nevertheless, Osiris occupied himself with the afterlife and with judging souls; his wife Isis, was a protective sorceress for families; the sky god Horus, his son, was known to reside within every pharaoh. Anubis, who had the head of a jackal, guided the dead and also attended to mummification. Ma’at, standing for truth and balance, sustained the order of the world.
Others, even more powerful, were Thoth, god of wisdom and writing; Hathor, goddess of love and joy; and Bastet, cat-headed goddess of home protection. Sekhmet brought war and healing; Set brought chaos. Amun, Nut, Geb, and Khnum were those controlling the sky, earth, water, and even life. These gods defined Egyptian religion, culture, and daily existence for thousands of years.

Top 15 Important Gods in Egyptian Mythology
-
Ra – Sun God
-
Osiris – God of the Afterlife
-
Isis – Goddess of Magic and Family
-
Horus – God of the Sky and Kingship
-
Anubis – God of Mummification
-
Thoth – God of Wisdom and Writing
-
Ma’at – Goddess of Truth and Balance
-
Set (Seth) – God of Chaos and Desert
-
Hathor – Goddess of Love and Joy
-
Bastet – Goddess of Protection and Cats
-
Sekhmet – Goddess of War and Healing
-
Khnum – God of Creation and the Nile
-
Amun (Amun-Ra) – King of the Gods
-
Nut – Goddess of the Sky
-
Geb – God of the Earth
3- Temples: Homes For The Religion of the Ancient Egyptian Gods
In the land of the Pyramids, the temples were mainly made for prayer to the gods. Therefore, each great temple was built for a certain god or goddess, with the Egyptians believing that the spirit of that god resided there. The Egyptian people were always trying to please the gods; carefully designed and filled with statues, paintings, and offerings to please the gods, or offerings, which would be requested from the gods. Only the priests and the Pharaoh could enter the inner chambers, where they gave offerings and started to say prayers to the gods inside.
The outer courts were open to the general public, who also came to worship, make offerings, or seek assistance. Temples had multiple uses: storing grain, holding festivals, and serving as centers for learning and healing. Some well-known temples such as Karnak, Luxor, and Abu Simbel still stand and speak of the importance religion of Egypt held in Ancient Egypt. The temples were how these people centered sacred buildings became the hub of the community life and the whole spiritual life of their people, again very symbolic of the close relationship between the gods and the people.
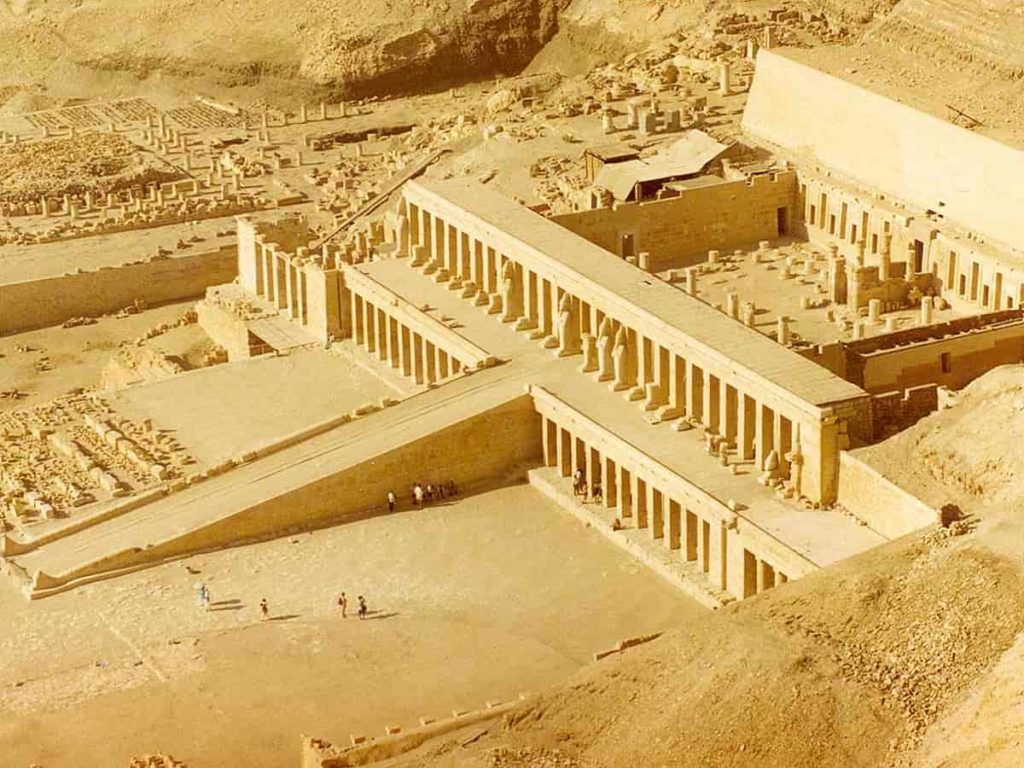

4- Priests and Their Role in Society
The Egyptian priests were extremely important people. Theirs was not merely a priestly role of praying for the people; they also maintained the temples and attended to the satisfaction of the gods. Priests would cleanse the statues of the gods daily, offer foodstuffs and perfumes, and chant special prayers. It was believed that peace would prevail in the land and crops would flourish if the gods were pleased.
Only behind the sacred temple doors could the priests be found. There, it was believed the spirit of the god resided: purity, clean linen clothing, and strict habits were expected from the priests to be near the gods. Some priests also studied astrology, medicine, and magic; they would help the pharaoh in making decisions.
When it comes to temple affairs, the priests were acting as teachers and advisors. Moreover, they do religion for the people and lead them, and give consultation on life issues. Their knowledge gave them great respect, and the people gave them status in Egyptian society. That is to say, the priests were guardians of life balance, thereby greatly affecting beginning and continuing life in Egyptian culture.
Imhotep was one of the most famous priests. He lived around 2700 BCE during the Old Kingdom. Additionally, he lived under the reign of Pharaoh Djoser. He was a high priest of the sun god Ra at Heliopolis, and he was also a brilliant architect, physician, and advisor. One of the most famous works was designing the Step Pyramid of Djoser at Saqqara, the first pyramid ever built in Egypt using stone.
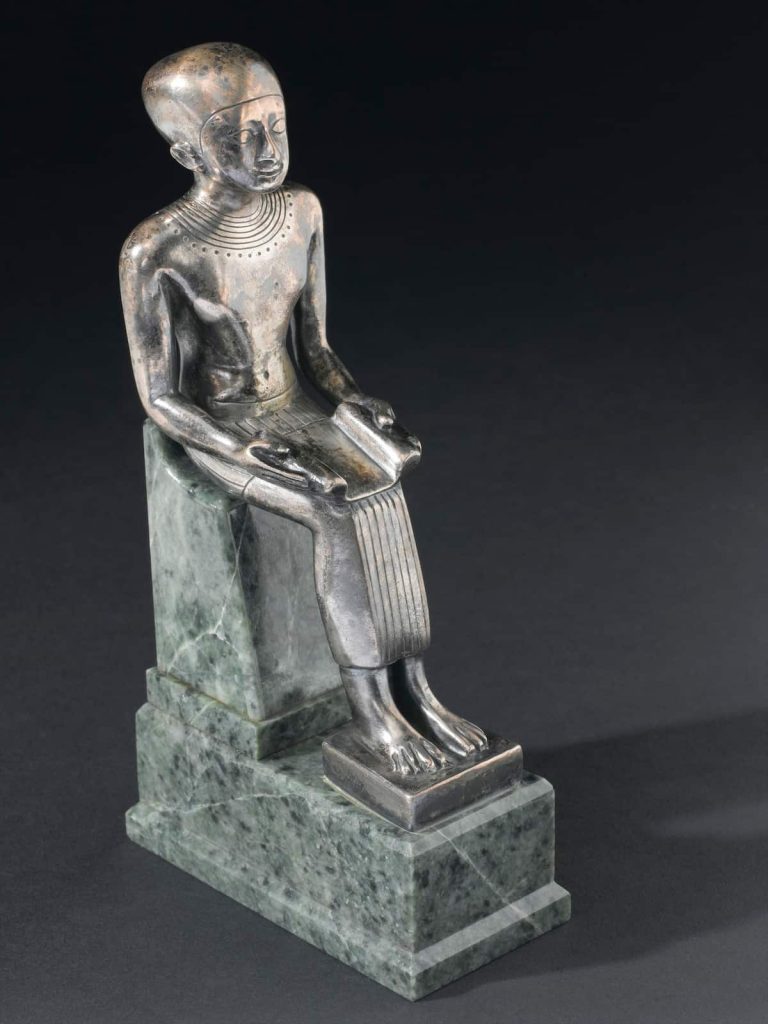

5- Daily Life and Religion of Ancient Egyptians
The ancient Egyptians’ religion of Egypt was part of daily life. And this is an ancient Egypt Facts about the daily life of a simple ancient Egyptian man. Additionally, they believed the god they pray to is controlling everything around them. They control the Nile River, weather, health, and even life after death. Therefore, ancient Egyptian people prayed, gave offerings, and followed rituals to keep the gods happy. When you look inside any of the simple houses or great palaces in ancient Egypt, you will find some small shrines where families could pray.
The ancient Temples were the center of religious life. Only priests could enter the sacred areas where the gods were believed to live. When you look at the gods of Egypt, you will see Ma’at, a belief in order, truth, and justice. Moreover, simple things like working in the fields or raising children were seen as part of honoring the gods. Another aspect of daily life was Festivals, music, and dancing. Ancient Egyptian games and musical entertainments were also ways people celebrated their religion.
Lastly, the religion of Egypt shaped how Egyptians lived, worked, and treated others. From Pharaohs to farmers, everyone believed that respecting the gods would bring peace and success.
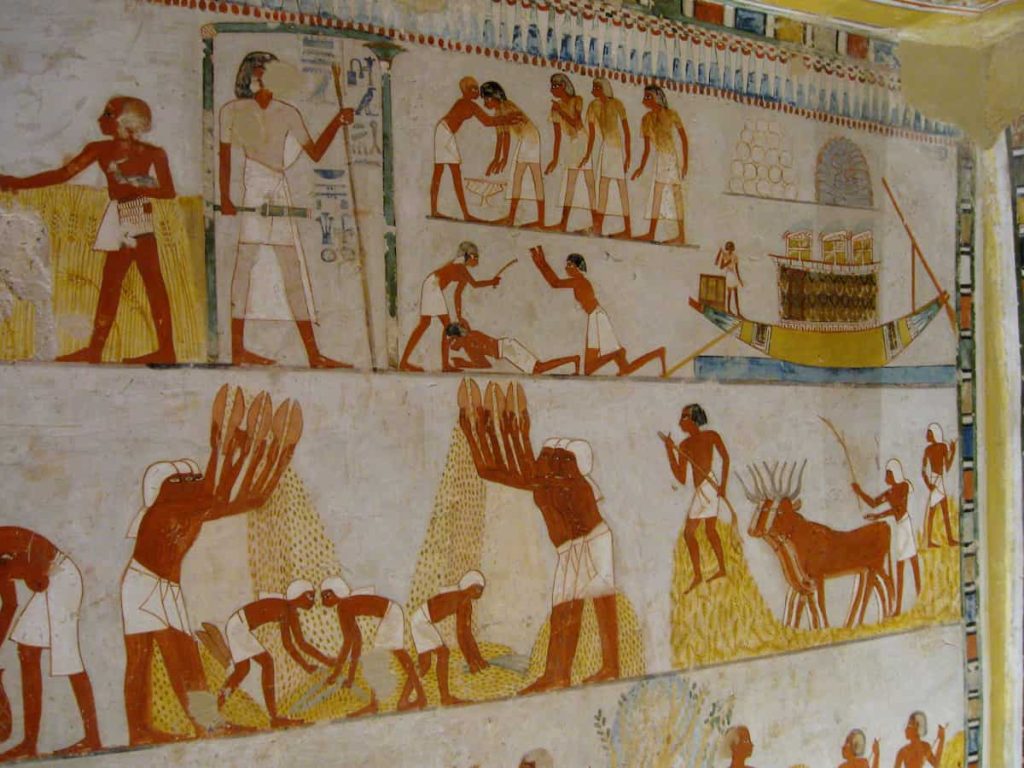

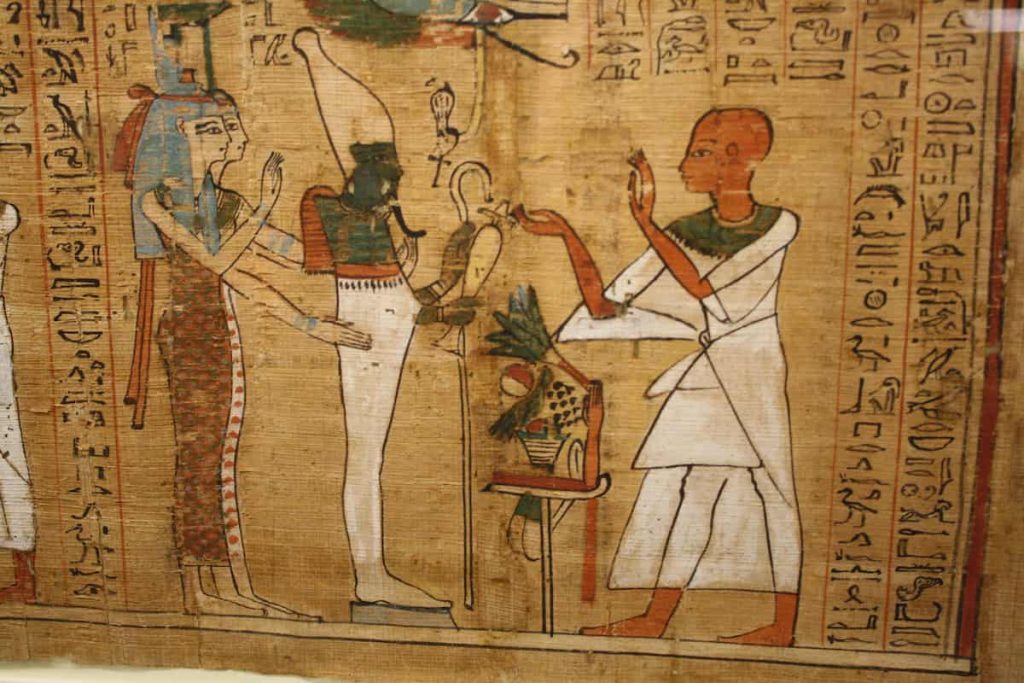
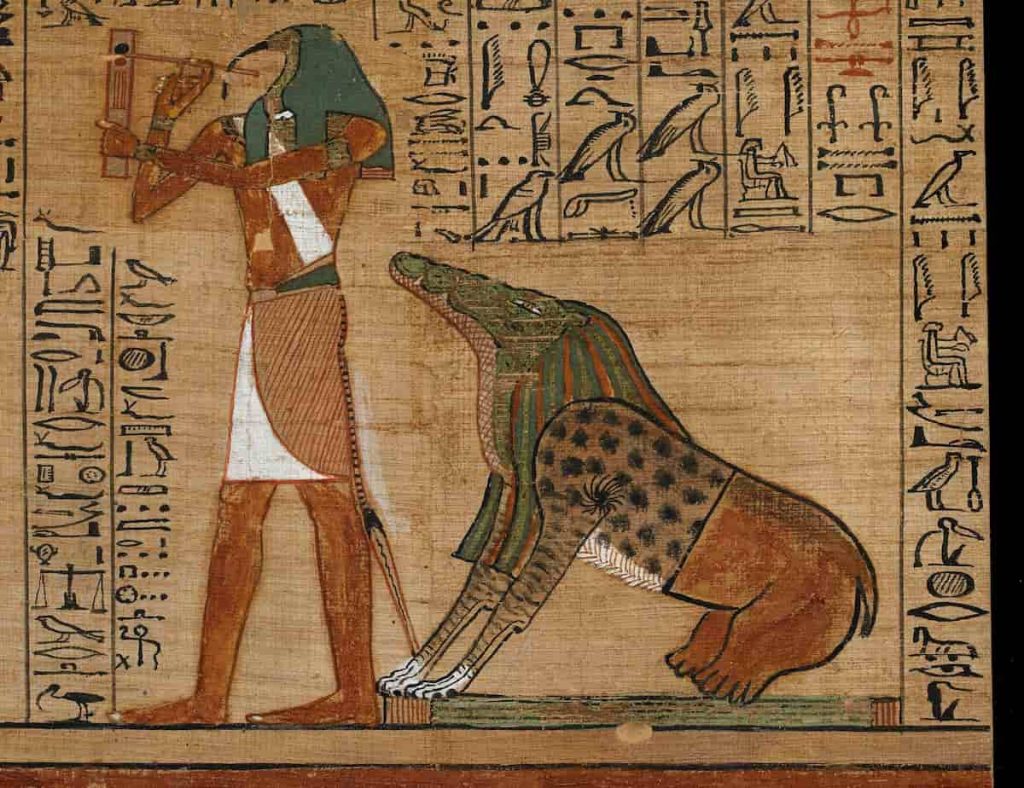
6- The Afterlife and the Journey of the Soul
Death for Egyptians has a different meaning. The Ancient Egyptians strongly believed in life after death. They thought that when a person died, their soul began a long journey to the afterlife, a peaceful and happy place called the Field of Reeds. The road to this Field of Reeds wasn’t easy. The soul had to pass many tests, including the famous weighing of the heart. In this test, the god Anubis weighed the heart against the feather of Ma’at, the symbol of truth and justice. If the heart was light and free of sins, the soul was allowed to live forever in the afterlife. But if it was heavier than the feather, then it was eaten by a scary creature called Ammit, and the soul would disappear forever.
In order to prepare for this long journey, your body must be protected first through mummification to protect the body. The practice was to place amulets for protection and fill tombs with food, treasures, and prayers. Additionally, the Egyptians believed the soul needed these things to survive in the next world. Lastly, you will see that the death wasn’t the end, but a new beginning, and they spent much of their lives making sure they would be ready for it.
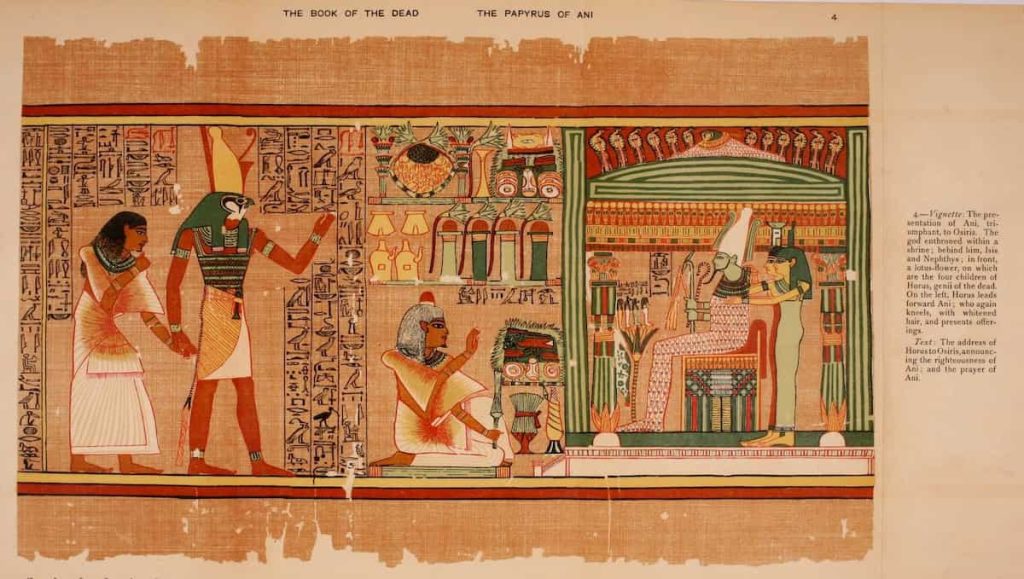
7- Mummification and Burial Customs
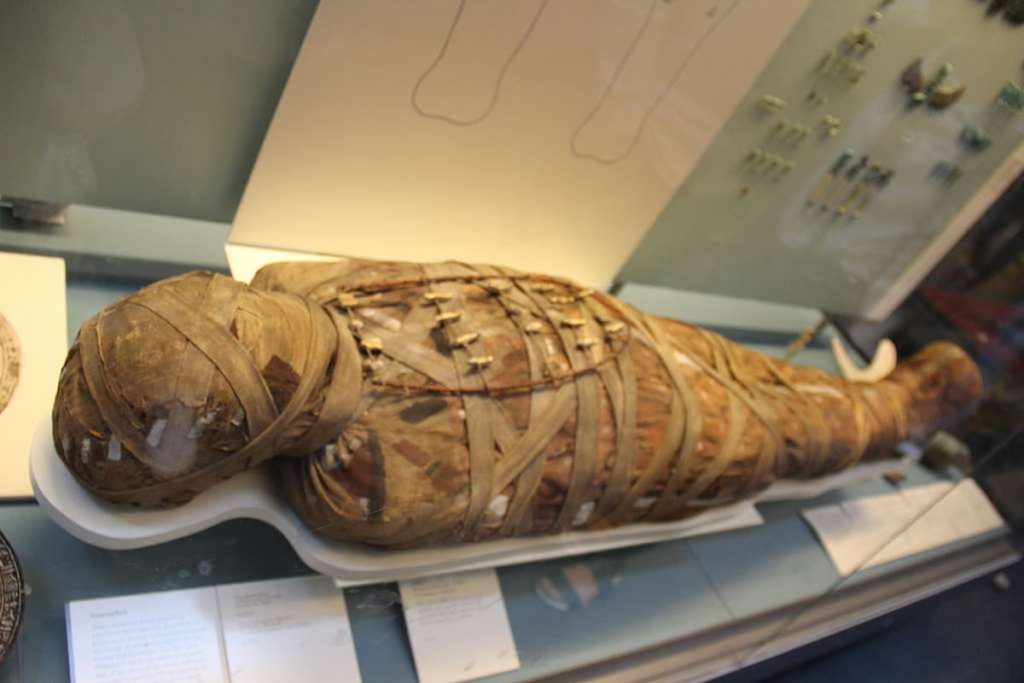
In Ancient Egypt, the Egyptian people believed in life after death. They thought that when a person died, their soul began a long journey to the afterlife. Therefore, they knew that they must protect the whole body to arrive the afterlife safely. Moreover, the body had to be protected after death so the soul could live on in the afterlife. The process of preserving the organs of the body is known as mummification. It is a process of keeping the body from rotting.
First, they remove the organs of the body and put them in canopic jars. Then, they dried the body with salt and wrapped it in linen cloth. Special spells and amulets were added to protect the person on their journey.
The second thing, after the mummification, the body is taken and placed in a coffin and buried in a tomb. This process doesn’t take place for the rich people. Moreover, the ancient Egyptians used to fill the tomb with food, jewelry, furniture, and everything the deceased might need in the afterlife. Additionally, the tombs’ walls were often painted with colorful scenes like what we see in the Valley of the Kings, which shows what daily life for an Egyptian was like.
But when it comes to the Poorer Egyptians, they had simpler burials. The main goal of mummification was to keep the body safe from any harm and help the soul to pass safely into the next world.

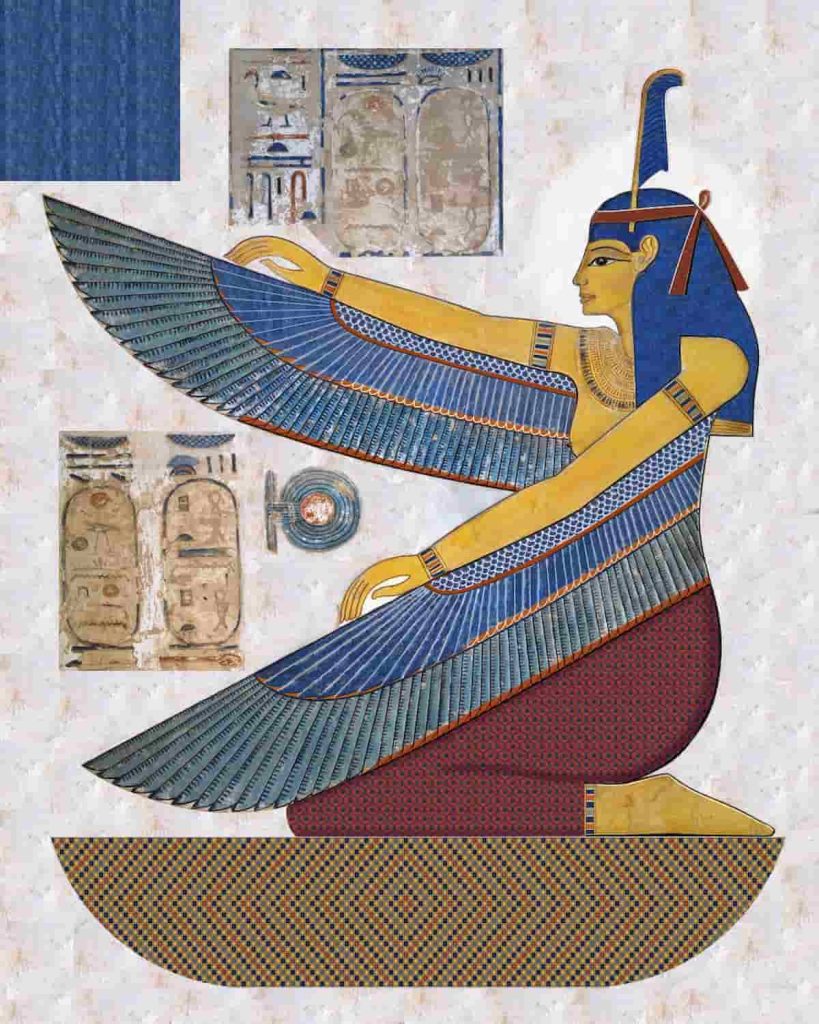
8- The Meaning of Maat: Truth and Balance
Ma’at was one of the most important ideas in Ancient Egypt. Moreover, she was the main figure and represented truth, justice, order, and balance. They believed that those who followed ma’at and obeyed her, the whole world works for him, and everything works smoothly for him. This means being honest, fair, and living in harmony with others and nature.
Besides, the Pharaoh also had to stay close to Ma’at. She was seen as the one who kept balance in both society and the natural world. Judges, priests, and even regular people were expected to act with fairness and kindness to help keep this balance.
Ma’at also plays a crucial role in the afterlife, as when someone dies, their heart is weighed against Ma’at’s feather. The heart of the descended must be lighter than the feather of ma’at to pass the test. This means that this descendant has a pure heart, and then he can rest in peace forever. On the other hand, if the heart were heavier than the feather, then the descendant is a sinner and his soul is lost.
Ma’at was meant to help the Egyptians live a balanced life full of peace and mercy. The Egyptians live better lives by reminding them to do what is right. It was the center of their laws, beliefs, and everyday choices.

9- Symbols and Sacred Animals in Religion
The Ankh symbol was a symbol that represented life for ancient Egyptians. Meanwhile, the eye of Horus represents protection and healing. Additionally, the Ancient Egyptians’ religion of Egypt used to have symbols and animals that played a big part in shaping the ancient Egyptians’ civilization. Therefore, you will find some drawings on the walls of the temples containing some animals and symbols. Additionally, each god and goddess in ancient Egypt was connected somehow to signs or creatures. These symbols were used in art, temples, jewelry, and even writing to show who the gods were and what they did.
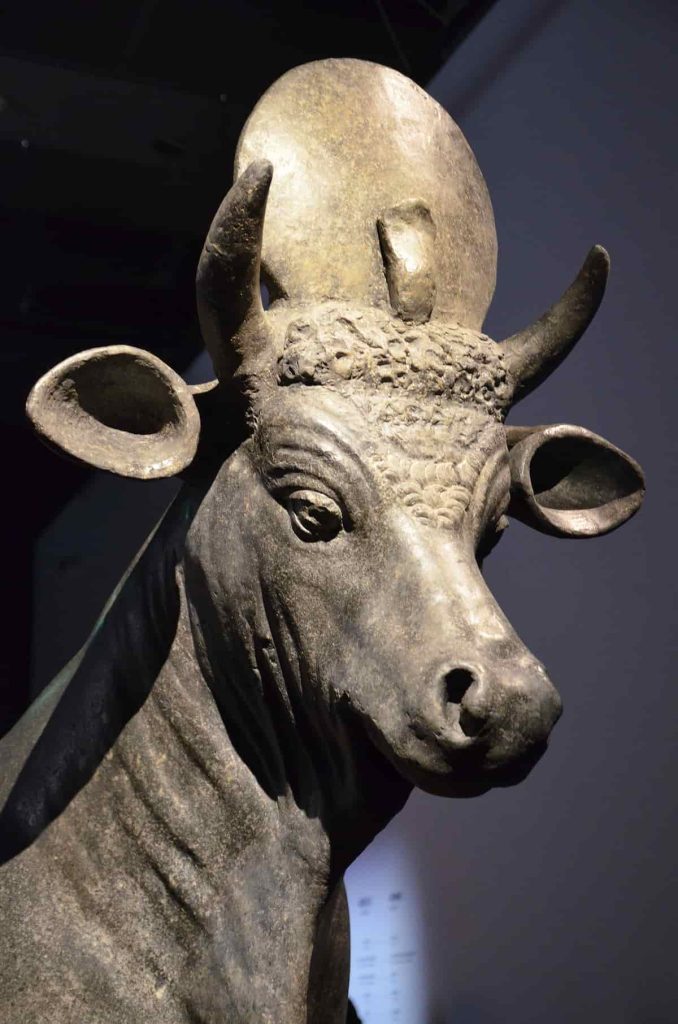
The scarab beetle was a sign of rebirth, and people wore it for good luck. As well as, The cat was linked to the goddess Bastet. The Goddess Bastet represents grace and protection. Additionally, more Egyptian symbols are connected to different gods. When you read about the falcon that represents Horus, you will find that he is the symbol of the sky, while the jackal is a symbol of Anubis, known as the god of mummification. Cows, ibises, crocodiles, and lions were also connected to different gods.
Lastly, symbols and animals are not just decorations; they are deeply connected to the religion of the ancient Egyptians and their beliefs.